Introduction
What Are the Types of Network Security? In today’s digital age, network security plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, preventing cyberattacks, and ensuring seamless communication. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations and individuals must implement robust security measures to protect their networks. What Are the Types of Network Security? But what are the types of network security? Let’s explore the various forms of network security that help safeguard information systems.

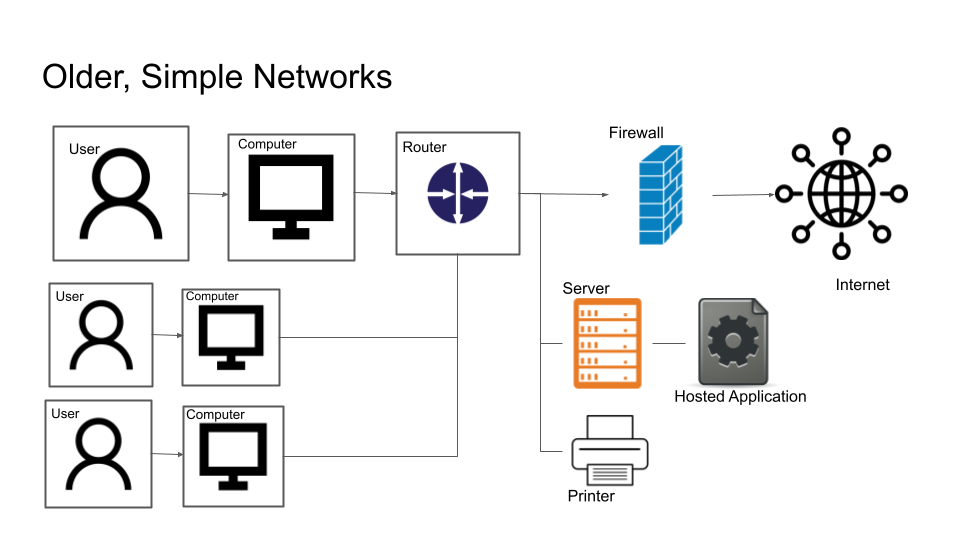
1. Firewall Security
A firewall acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Firewalls can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both. They help prevent unauthorized access and filter malicious traffic.
2. Antivirus and Anti-Malware Protection
Antivirus and anti-malware software detect, prevent, and remove malicious software, including viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. What Are the Types of Network Security? These tools constantly scan files, applications, and network traffic to identify and neutralize threats before they can cause damage.
3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) monitor network traffic for signs of suspicious activity. While IDS detects and alerts administrators about potential threats, IPS actively blocks malicious traffic to prevent attacks from spreading within the network.
4. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
A VPN encrypts data transmitted over the internet, providing a secure connection between remote users and the organization’s network. VPNs are commonly used to protect sensitive data, especially when employees work remotely or access company resources from public Wi-Fi networks.

5. Access Control and Authentication
What Are the Types of Network Security? Access control mechanisms ensure that only authorized users can access specific network resources. Authentication methods, such as usernames and passwords, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication (MFA), add extra layers of security to prevent unauthorized access.
6. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions prevent the accidental or intentional leakage of sensitive data. These systems monitor data in transit, at rest, and in use, ensuring that confidential information is not sent outside the organization without authorization.
7. Email Security
Remains a primary target for cyberattacks, including phishing scams and malware distribution. Email security solutions use encryption, spam filters, and advanced threat-detection techniques to prevent malicious emails from reaching users’ inboxes.
8. Wireless Security
Networks are more vulnerable to cyber threats due to their open nature. Wireless security measures include WPA3 encryption, secure access points, and network segmentation to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
9. Cloud Security
With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, securing cloud-based data and applications has become a priority. Cloud security involves encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to protect sensitive data stored in cloud environments.
10. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides a network into smaller subnetworks to limit the spread of cyber threats. By isolating critical assets and restricting user access, segmentation enhances security and minimizes the impact of a potential breach.

11. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM solutions collect and analyze security data from multiple sources in real-time. What Are the Types of Network Security? They provide centralized visibility into security events, helping organizations detect and respond to threats more effectively.
12. Web Security
Web security measures protect users from cyber threats when browsing the internet. These solutions include web filtering, secure web gateways, and HTTPS encryption to block malicious websites and prevent data theft.
13. Endpoint Security
Endpoint security focuses on securing devices such as computers, mobile phones, and IoT devices that connect to the network. It includes antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and application control to protect against cyber threats.
14. Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust is a security framework that requires strict verification for every user and device attempting to access network resources. It follows the principle of “never trust, always verify” to prevent unauthorized access and insider threats.
15. Behavioral Analytics Security
Behavioral analytics security uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect unusual activities within a network. By analyzing user behavior patterns, it can identify potential threats and prevent cyberattacks before they occur.
16. Mobile Device Security
With the rise of mobile computing, securing mobile devices is essential. Mobile security includes encryption, remote wiping capabilities, and mobile threat defense (MTD) solutions to protect sensitive data on smartphones and tablets.
Why is Mobile Device Security Important?
Mobile devices store sensitive personal and professional data, including emails, contacts, financial information, and passwords. A security breach can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and exposure to confidential business data.
Key risks include:
- Data Theft – Hackers can steal personal or business data.
- Malware & Viruses – Malicious software can harm your device and data.
- Phishing Attacks – Fraudulent emails and messages trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Device Theft or Loss – Stolen or lost phones can lead to unauthorized access.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks – Public networks can be exploited by hackers.
Key Mobile Security Threats
- Malware & Spyware – Malicious apps that can track activities and steal information.
- Phishing Attacks – Fake websites or messages that trick users into entering sensitive details.
- Unsecured Apps – Apps with weak security can expose data.
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping – Cybercriminals intercept data over public Wi-Fi.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks – Hackers intercept communication between users and services.
- Physical Theft – A stolen or lost device can lead to data compromise.
Best Practices for Mobile Device Security
1. Use Strong Authentication
- Set a strong password, PIN, or biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition).
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for extra security.
2. Keep Software & Apps Updated
- Regularly update the operating system (iOS, Android) and apps to fix security vulnerabilities.
- Avoid using outdated or unsupported devices.
3. Install Security Software
- Use antivirus and anti-malware apps to protect against threats.
- Enable Find My Device (Android) or Find My iPhone (Apple) to track lost or stolen devices.
4. Be Cautious with App Downloads
- Download apps only from official stores (Google Play, Apple App Store).
- Check app permissions before installing.
5. Avoid Public Wi-Fi or Use VPN
- Public Wi-Fi can be insecure; avoid accessing sensitive information on it.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for encrypted communication.
6. Encrypt Your Data
- Enable device encryption to protect stored data.
- Use secure messaging apps that support end-to-end encryption.
7. Be Aware of Phishing & Scams
- Do not click on suspicious links in emails or messages.
- Verify sender details before providing personal information.
8. Enable Remote Wipe & Lock
- If your device is lost or stolen, use remote wipe features to erase data.
- Lock your device to prevent unauthorized access

Enterprise Mobile Security Measures
For businesses, securing mobile devices is crucial for protecting company data. Organizations should:
- Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) to control device security.
- Require VPN usage for remote workers.
- Train employees on cybersecurity best practices.
Conclusion
Future Trends in Network Security
As technology continues to advance, network security must also evolve to counter new cyber threats. Emerging trends include AI-driven security, quantum cryptography, blockchain security solutions, and more advanced threat intelligence systems. Organizations should stay proactive and continuously adapt their security strategies to protect their networks from ever-evolving cyber threats.

Read More: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
FAQs
Network security protects a network from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
It safeguards sensitive data, prevents cyber attacks, and ensures smooth network operations.
A firewall acts as a barrier, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules.
A VPN encrypts internet traffic, securing connections and protecting data from hackers.
MFA requires users to verify their identity using multiple authentication methods.
Cyber threats include malware, phishing, ransomware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and insider threats.
It scans and removes malicious files, preventing virus infections on devices.
Zero Trust requires continuous verification of users and devices to prevent unauthorized access.
It divides a network into smaller sections to limit the impact of cyber threats.
By using firewalls, encryption, antivirus software, and implementing strong security policies.
IDS detects threats, while IPS actively blocks malicious activities.
It prevents phishing, spam, and malware from reaching users’ inboxes.
Use strong passwords, enable MFA, update software, and educate employees on cybersecurity.
It protects individual devices from cyber threats and malware infections.
It includes encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring of cloud environments.
Risks include data theft, malware infections, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.

